Cloud Computing Deployment Models: Technical know how.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
 |
| Cloud deployment models |
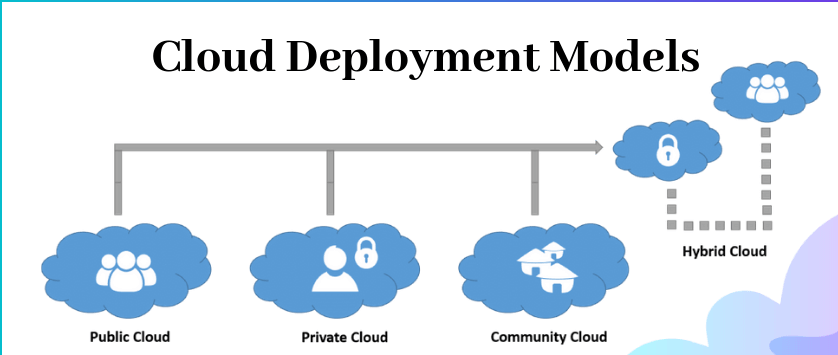
What are the most popular cloud deployment models? There are four types of them: public, private, hybrid and community clouds. Additionally, there are also distributed clouds, multiclouds, poly clouds and other models, but they are not so widespread.
As cloud technology is providing users with so many benefits, these benefits must have to be categorized based on users requirement. Cloud deployment model represents the exact category of cloud environment based on proprietorship, size, and access and also describes the nature and purpose of the cloud. Most organizations implement cloud infrastructure to minimize capital expenditure & regulate operating costs.
Full article: http://entradasoft.com/blogs/cloud-computing-deployment-models-technical-know-how
About deployment model
Public Cloud
Public Cloud is a type of cloud hosting that allows the accessibility of systems & its services to its clients/users easily. Some of the examples of those companies which provide public cloud facilities are IBM, Google, Amazon, Microsoft, etc. This cloud service is open for use. This type of cloud computing is a true specimen of cloud hosting where the service providers render services to various clients
Server infrastructure belongs to service providers that manage them and administer pool resources, which is why there is no need for user companies to buy and maintain their hardware. Provider companies offer resources as a service both free of charge or on a pay-per-use basis via the Internet connection. Users can scale resources when required.
The public cloud deployment model is the first choice for businesses that operate within the industries with low privacy concerns. When it comes to popular public cloud deployment models, examples are Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) the top service provider, Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine, IBM Cloud, Salesforce Heroku and others.
Advantages:
- Flexible
- Reliable
- High Scalable
- Low cost
- Place independence
Disadvantages:
- Less Secured
- Poor Customizable
Private Cloud
There is little to no difference between a public and a private model from the technical point of view, as their architectures are very similar. However, opposed to a public cloud that is available to the general public, only one specific company owns a private one. That is why it is also called an internal or corporate cloud.
‘Internal Cloud’ means that it allows the accessibility of systems and services within a specific boundary or organization. The cloud platform is implemented in a cloud-based secure environment that is guarded by advanced firewalls under the surveillance of the IT department that belongs to a particular organization. Private clouds permit only authorized users, providing the organizations greater control over data and its security. Business organizations that have dynamic, critical, secured, management demand based requirement should adopt Private Cloud.
Advantages:
- Highly private and secured: Private cloud resource sharing is highly secured.
- Control Oriented: Private clouds provide more control over its resources than public cloud as it can be accessed within the organization’s boundary.
Disadvantages:
- Poor scalability: Private type of clouds is scaled within internal limited hosted resources.
- Costly: As it provides secured and more features, so it’s more expensive than a public cloud.
- Pricing: is inflexible; i.e., purchasing new hardware for up-gradation is more costly.
- Restriction: It can be accessed locally within an organization and is difficult to expose globally.
Community Cloud
A community deployment model largely resembles a private one; the only difference is the set of users. While a private type implies that only one company owns the server, in the case of a community one, several organizations with similar backgrounds share the infrastructure and related resources. Example of such a community is where organizations/firms are there along with the financial institutions/banks. A multi-tenant setup developed using cloud among different organizations that belong to a particular community or group having similar computing concern.
For joint business organizations, ventures, research organizations and tenders community cloud is the appropriate solution. Selection of the right type of cloud hosting is essential in this case. Thus, community-based cloud users need to know and analyze the business demand first.
Advantages:
· Cost reduction
· Improved security, privacy and reliability
· Ease of data sharing and collaboration
Disadvantages:
· High cost if compared to a public deployment model
· Sharing of fixed storage and bandwidth capacity
· It is not widespread so far
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud is another cloud computing type, which is integrated, i.e., it can be a combination of two or more cloud servers, i.e., private, public or community combined as one architecture, but remain individual entities. Non-critical tasks such as development and test workloads can be done using public cloud whereas critical tasks that are sensitive such as organization data handling are done using a private cloud. Benefits of both deployment models, as well as a community deployment model, are possible in a hybrid cloud hosting.
Hybrid cloud deployment model not only safeguards and controls strategically important assets but does so in the most cost- and resource-effective way possible for each specific case. Also, this approach facilitates data and application portability.
Advantages:
- Flexible
- Secure
- Cost Effective
- Rich Scalable
Disadvantages:
- Complex networking problem
- Organization’s security Compliance
Read More… http://entradasoft.com/blogs/cloud-computing-deployment-models-technical-know-how



Comments
Post a Comment